Dreaming the unrepressed unconscious and beyond: repression vs dissociation in the oneiric functioning of severe patients
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Accepted: 31 May 2021
Authors
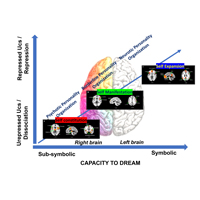
Starting with Freud and Jung, dreams have always been considered a core source of information for psychoanalysis. Nowadays, neuroscientific findings suggest that dreams are related especially to limbic and right emotional brain circuit, and that during REM stages they engage self-related and visual internally generated processing. These neuroscientific findings together with contemporary psychoanalysis suggest that dreams are related to the sense of self and serve the purpose of re-integrating and re-structuring the integrity of the psyche. However, while dreams are still viewed as ‘the via regia to the unconscious’, it is the unconscious that has been reconsidered. The repressed unconscious seems to be related with left brain activity while the unrepressed unconscious based on dissociation seems to be associated with limbic and cortical areas of the right hemisphere. This notion of the unconscious might be seen as an implicit self-system encoded in the right brain that evolves in the interaction with a primary caregiver developing through preverbal and bodily stages of maturation enhanced by signals of dual communication. What kind of dreams for which unconscious? What are the differences regarding the capacity to dream for neurotic and borderline personality organizations? Our research aims to integrate psychodynamics, infant research, and neuroscientific findings to better understand the role of dreams in the assessment and treatment of, especially, traumatized and borderline patients. The capacity to dream is here proposed as a sort of enacted manifestation of emotional memories for the development of a more cohesive, coherent and symbolic vs fragmented, diffuse and alexithymic sense of self.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






